at Sabancı Group
Capturing Light for a
Sustainable Future
Just as solar panels harness sunlight to generate clean energy, Sabancı Holding
channels sustainability principles into every facet of its operations. By absorbing
knowledge, adapting to new technologies, and continuously evolving, we ensure
that our business remains efficient, future-ready, and purpose-driven. Our focus
on renewable energy, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience enables
us to be a catalyst for a net-positive impact across industries.
Our Material Issues
To determine our material issues, we conducted a double materiality analysis, considering evolving international standards.
Initially, we compiled a comprehensive list of potential material issues through literature reviews, stakeholder consultations, and benchmarking against international standards. We also incorporated guidelines from various sources, such as:
- The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) double materiality guidance document.
- The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) material issues for the Asset Management and Banking sectors.
- MSCI ESG materiality map.
- S&P sustainability index criteria, including the Dow Jones Sustainability Index.
- The World Economic Forum 2024 Global Risk Report.
In parallel with these efforts, and considering feedback from global development and assessment organizations, we identified a total of eighteen material issues. Once we identified our material issues, we proceeded with a survey to our stakeholders through questionnaires created by our selected 18 material topics to be assessed by our internal and external stakeholders on a materiality basis.
We categorized our stakeholders, who are affected by Sabancı Holding's operations and with whom we actively collaborate throughout the fiscal year, into eight groups. After collecting the survey results, all stakeholder feedback and assessments were scored and weighed according to predetermined criteria. Additionally, using the SASB Four-Stage Impact Analysis, we evaluated financial impact and risks, legal impacts, potential to create competitive advantage, and innovation opportunities.
Through international standards, ESRS requirements, and literature review, we compiled a list of 152 risks and opportunities, and 114 positive and negative impacts relevant to all current and future issues for Sabancı Holding.
We assessed our sustainability impacts, risks, and opportunities across the entire value chain. These evaluations have been integrated into the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) process with the input of Sabancı Holding's Risk Department.
Double Materiality Matrix
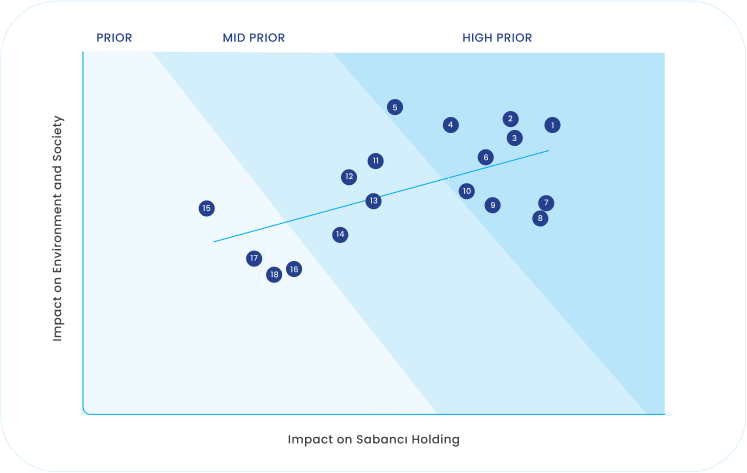
2 Climate Emergency
3 Circular Economy
4 Responsible Investment and Sustainable Business Models
5 Talent Management
6 Corporate Governance
7 Opportunity Management and Agility
8 Digital Technologies
9 Collaboration and Effective Communication with Stakeholders
10 Risk Management and Resilience
11 Innovation and R&D
12 Supply Chain Management
13 Reputation Management
14 Occupational Health and Safety
15 Social Contribution and Investments
16 Human Rights and Equal Opportunity
17 Biodiversity and Nature Positive Actions
18 Cyber Security and Data Privacy
The materiality assessment process at Sabancı Holding is verified by a third-party assurance provider to ensure the accuracy, credibility, and transparency of our evaluation. The results of our 2023 double materiality analysis were signed by the Holding Executive Committee and the Board Sustainability Committee.
In 2024, we reassessed our material issues to ensure they continue to reflect the key priorities of Sabancı Holding. The results confirmed that the existing materiality matrix remains valid and will continue to be used for the 2024 fiscal year. A comprehensive double materiality assessment will be conducted for the 2025 fiscal year, subject to approval by the Board Sustainability Committee and the Executive Committee, as well as third-party assurance.
Our Repsonse to Emerging Global Risks
We operate in an environment marked by intensifying uncertainty and diverging global trajectories. The rules of value creation are being reshaped by new regulatory paradigms, geopolitical tensions, and shifts in societal expectations.
Among the most urgent developments are the expansion of carbon pricing mechanisms, particularly in Türkiye and key export markets, and the growing polarization of ESG policies across the globe. These risks challenge not only the resilience of business models but also the consistency of long-term planning and stakeholder alignment.
At Sabancı Holding, we view risk not as a variable to be contained but as a strategic lens through which we navigate transformation. Emerging risks, whether regulatory, financial, environmental, or reputational, are interconnected and dynamic. They demand foresight, adaptability, and a consistent commitment to sustainability principles, even when external signals are fragmented or contradictory.
Our governance framework ensures disciplined oversight and coordinated response. The Board of Directors, supported by the Board Sustainability Committee, the Early Detection of Risk Committee, and the Audit Committee, plays a central role in this effort. The Sustainability Leadership Committee fosters executive-level alignment across Group companies, while the Investment Committee integrates ESG criteria and transition risks into capital allocation decisions.
This integrated model allows us to evaluate risks holistically across sectors and geographies and to translate early signals into informed action. We apply this model to navigate two emerging challenges in particular: the rollout of emissions trading and carbon border regulations in Türkiye and the European Union, and the increasingly fragmented global discourse around ESG. Both issues have direct implications for our portfolio, investment planning, and access to markets.
In response, we continue to strengthen our organizational capacity to address regulatory uncertainty, shifting market expectations, and sustainability challenges. This includes enhancing scenario analyses, expanding science-based climate targets across subsidiaries, investing in scalable low-carbon solutions, and reinforcing ESG data infrastructure in line with local and global regulations, and other global standards. At the same time, we maintain close engagement with global investors, reaffirming our long-term view of sustainability as a source of resilience and competitive advantage.
These emerging risks are directly linked to a broad set of material issues identified by Sabancı Holding, including Corporate Governance, Reputation Management, Financial Performance, Responsible Investment and Sustainable Business Models, Opportunity Management and Agility, Risk Management and Resilience, and Collaboration and Effective Communication with Stakeholders. By connecting risk management practices with these material topics, we ensure that our strategy remains both opportunity-driven and impact-aware.
At Sabancı Holding, we see leadership not as a title but as a commitment to act decisively in the face of uncertainty. Resilience today means embedding risk into strategy and sustainability into governance. It means responding with agility to evolving dynamics while building the systems, culture, and partnerships needed for long-term success. And it means moving forward with clarity, transparency, and a deep sense of responsibility toward all stakeholders. In doing so, we aim not only to preserve value but to create it ethically, inclusively, and for the long term.
With the recent enactment of the Climate Law by the Turkish Parliament, Türkiye has taken a major step toward building a solid regulatory framework to support its net-zero targets and align with the European Green Deal. The law establishes the legal foundation for the launch of a national Emissions Trading System (ETS), which will introduce carbon pricing in key sectors, starting with emissions intensive industries such as cement and energy businesses where Sabancı Holding has a strong presence.
The ETS will require companies to monitor, report, and meet their emission obligations through the purchase and surrender of allowances, highlighting the growing importance of effective carbon management and compliance systems.
In addition, Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) presents a transition risk for Sabancı Holding, particularly in energy-intensive business lines with export exposure to the EU. Embedded carbon reporting requirements and the upcoming cost of carbon certificates may increase operational expenses and reduce competitiveness. The risk is more pronounced in areas where low-carbon production technologies are not yet fully scalable.
While regulatory frameworks such as the EU ETS and CBAM initially originated in Europe, similar carbon pricing mechanisms are now rapidly expanding across other regions, including Asia and Türkiye. This global shift toward regulated carbon markets poses increasing cost pressures and compliance requirements for emissions-intensive sectors such as cement and energy businesses where Sabancı Holding has significant operations and which collectively accounted for 24% of its total revenue as of year-end 2024. This evolving regulatory landscape compels Sabancı Holding to proactively align with emerging climate-related regulations, not only to maintain its competitiveness in international markets, but also to preserve its license to operate domestically as Türkiye’s climate policy framework continues to develop. The primary risks stem from rising carbon costs, increased compliance obligations, and potential limitations in market access for high-emission products.
To address the growing regulatory risks associated with emerging carbon market mechanisms, particularly Türkiye’s ETS and the EU CBAM, Sabancı Holding has implemented a structured and forward-looking risk management approach across its portfolio. All Group companies that are either currently within scope or are likely to be affected by these mechanisms have conducted detailed scenario analyses to assess potential financial and operational impacts under various carbon pricing trajectories. These analyses guide strategic decision-making and inform the design of tailored decarbonization pathways, supporting the Group’s transition planning efforts.
A significant number of Sabancı Holding’s subsidiaries have already set Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) aligned emission reduction targets. These companies are prioritizing investments in low-carbon technologies, energy efficiency, and clean energy solutions as part of their long-term strategies. This proactive stance has enhanced the Group’s regulatory readiness while enabling it to mitigate potential compliance costs and maintain competitiveness in both domestic and international markets with increasingly stringent climate policies.
To further support implementation, Sabancı Holding continues to strengthen its carbon data infrastructure, digital systems, and reporting capabilities. A centralized and harmonized ESG reporting framework, aligned with local and global regulations and standards, enables transparent, verifiable, and decision-useful sustainability disclosures across all Group companies. These efforts are supported by ongoing investments in digital ESG infrastructure, which reduce operational complexity and enhance data integrity.
Sabancı Holding’s governance model embeds sustainability into decision-making at the highest level. Oversight is provided by the Board of Directors, while implementation is coordinated by the Group Sustainability Directorate. ESG performance is increasingly integrated into executive remuneration, capital allocation, and risk management processes, reinforcing internal accountability.
- Financial Performance
- Responsible Investment and Sustainable Business Models
- Innovation and R&D
- Risk Management and Resilience
The global ESG landscape is entering a more complex and fragmented phase as political and regulatory dynamics shift across key markets. In the United States, ESG-related practices have faced growing backlash. Several states have introduced or proposed legislation that challenges the integration of ESG considerations in investment and corporate decision-making. Critics argue that ESG may conflict with fiduciary duty or reflect politically motivated agendas, and this sentiment is gaining influence in both political discourse and financial policy.
In parallel, the European Union, long considered a frontrunner in sustainability regulation, has signaled a more cautious stance. The recently introduced Omnibus Regulation includes revisions aimed at simplifying and, in certain cases, reducing ESG disclosure obligations. This move reflects increasing sensitivity to regulatory burden and implementation challenges, suggesting that even the most ambitious jurisdictions are re-evaluating the pace and scope of ESG-related rulemaking.
In this environment, companies are finding themselves on slippery ground, unsure of how their sustainability efforts will be interpreted or received by different stakeholders. As ESG becomes more politically charged, organizations must navigate this landscape with caution, balancing their long-term sustainability goals against short-term external pressures and uncertainty.
The increasing polarization of the global ESG landscape introduces a strategic risk that may directly affect Sabancı Holding’s long-term investment planning, access to incentives, and alignment with evolving regulatory expectations. In the United States, the growing backlash against ESG-related practices has led to legislative uncertainty in several states. This may create potential inconsistencies in the implementation or continuity of major federal-level policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which currently offers significant incentives for clean energy and climate technologies. For Sabancı Holding, which has ongoing and planned investments in renewable energy in the U.S. and globally, any weakening or reversal of such incentive schemes may alter expected return profiles, affect capital allocation decisions, or delay project timelines.
Similarly, the European Union’s recent efforts to moderate ESG disclosure requirements, while aiming to reduce administrative burden, may lead to a fragmented regulatory landscape that challenges consistent reporting and comparability across jurisdictions. This could increase the complexity and cost of compliance for multinational companies due to differing levels of expectations around reporting scope.
Overall, the divergence in ESG policies across key markets increases uncertainty in regulatory planning, financial forecasting, and stakeholder engagement. This dynamic may influence Sabancı Holding’s portfolio strategies, expansion decisions, and its ability to leverage sustainability-linked financing instruments.
Sabancı Holding acknowledges the growing polarization around ESG topics but believes that sustainability continues to offer significant opportunities for long-term value creation. Sabancı Holding views this transition not as a constraint, but as a catalyst for innovation and competitive advantage.
To reinforce this belief, the Holding maintains continuous, transparent engagement with institutional investors and stakeholders. Through initiatives such as ESG-focused roadshows, dedicated ESG Days, and investor visits, Sabancı Holding shares its strategic direction, performance, and sustainability roadmap. These efforts have reaffirmed that investors largely continue to approach ESG from an opportunity-driven lens.
Despite growing ESG polarization, Sabancı Holding continues to view sustainability as a strategic opportunity especially in areas with strong return potential like energy business. Rather than stepping back, the Holding focuses on targeted investments where sustainability and financial performance go hand in hand.
For instance, Sabancı Renewables increased its portfolio to 504 MW in US, advancing its position in utility scale clean energy. These efforts align with global trends, such as the IEA’s forecast that renewables will account for 35% of global power generation by 2025 demonstrating that sustainability, when focused and strategic, continues to create value even in a polarized ESG environment.
- Corporate Governance
- Reputation Management
- Financial Performance
- Responsible Investment and Sustainable Business Models
- Opportunity Management and Agility
- Risk Management and Resilience
- Collaboration and Effective Communication with Stakeholders
 | Sustainability for a Better Life 2024 Report
| Sustainability for a Better Life 2024 Report